MINING IN ZAMBIA A. What is mining?
It is the extraction (removal) of minerals from underground. e.g copper
B. METHODS OF MINING
The following are the methods of mining Open pit mining
Ø This is a method of mining minerals which are nearer to the ground surface. Example of open pit mine .in Zambia is the Nchanga open pit mine in Chingola and it is the biggest open pit in Zambia. This method is also used by mining companies in North Western province Advantages of open pit mining
- It is cheaper because it does not require heavy and sophisticated machinery Disadvantages
- It poses a danger to the environment. The mining may get flooded
- Humans or people are also displaced when such mines are opened
- Pollutes surface water and underground
- Causes landslides
Underground (shaft) mining
This is the method of mining minerals which are very deep in the ground. The shaft or machines are sunk and fitted with sharp objects to create a route to reach out the minerals in the ground and bring them out to the surface. Disadvantages of underground mining
- It is too expensive because it uses expensive and heavy machines Examples of underground mines
- Most of the mining towns have shaft mine like Nkana mine in Kitwe, Konkola mine in Chililabombwe and Mufulira mine in Mufulira.
Note: Mufulira Mine in Zambia is the largest underground mine in Zambia.
C.NAME THE MINING TOWNS (AREAS) IN ZAMBIA
Copperbelt province
The mining towns (areas) include:
- Ndola – Bwana mukubwa mine
- Mufulira – Mufulira plant
- Kitwe – Nkana mine
- Luanshya – Baluba mine
- Chambeshi – Chambeshi mine
- Chililabombwe – Konkola mine
North Western province
The North Western towns include Kasenshi,Lumwana, Kalengwa and Kalumbila.
Southern Province
The mining towns (areas) include Maamba and Munali
Central Province
The mining towns (areas) include Mkushi, Nampundwe and Kabwe (mines closed)
Lusaka Province
The mining towns (areas) include Chilanga and Rufunsa
Luapula Province
The mining towns (areas) include Mansa – Manganese and is not in operation
D.DESCRIBE THE COPPER PROCESSING IN ZAMBIA
This is a process in which copper goes through before being sold
- Mining: This is the first process which is the removal from the ground.
- Milling (crushing):This is the second process which is the crushing and turning copper into copper powder
- Smelting: This is the third process which is the removal of impurities (unwanted products)through filtration process
- Refining: This is the final process which is the purification making the copper cathodes.
E.NAME THE ROUTES FOR TRANSPORTING COPPER TO OTHER COUNTRIES
- Zambia to Tanzania– then to port of Dar es Salaam by rail line.
- Zambia to South Africa then to port of Dubai East London by railway line. (iii) Zambia to Mozambique to port of Maputo and Beira by road
F. IMPORTANCE OF MINING IN ZAMBIA
(i) It bring foreign exchange
(ii)It brings development e.groads ,schools
(iii)It provides or creates employment to people
(iv)It brings wealth to the country
(v)It provides material (raw) for many manufacturing industries e.g copper to make electric cables.
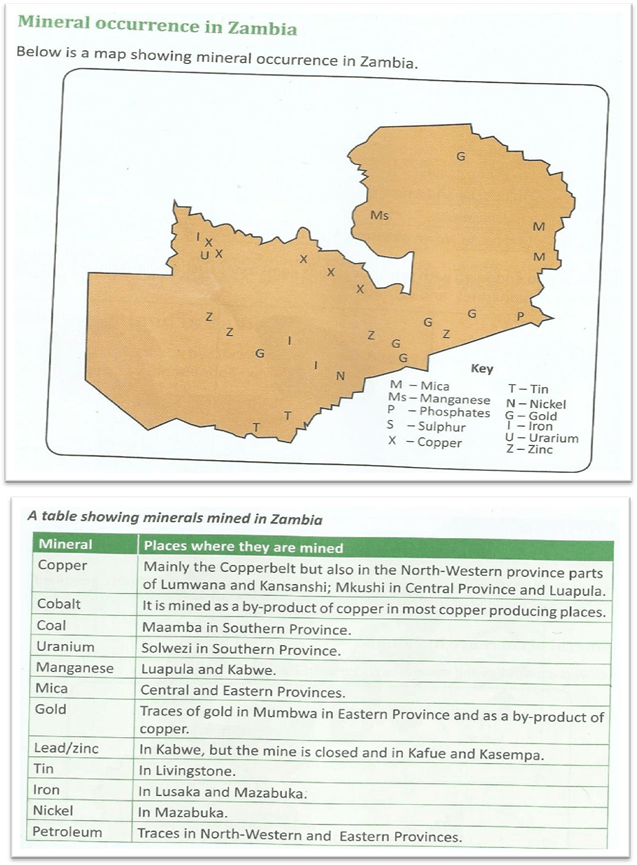
G. TYPES OF MINERALS MINED IN ZAMBIA
(i) Copper
It is mined in the Copperbelt, North Western and Central provinces of Zambia.
USES OF COPPER
- For making electrical cables
- For making bullets for guns
- For making coins ,radios and roofing materials
- For making water pipes and taps
- For making bronze and brass medals
- For making telephone ,radio and Television wires
- For making ornaments
DISADVANTAGES
- It is difficult to extract copper from the ground.
- High cost of production e.g buying of machinery
- Long distance to many sea ports
- Flactuating prices of copper on the world market
- Poor road network
- COBALT
Cobalt is mined as aby product of copper.This means it is mined at the same time when mining copper.Cobalt is mined at Nkana ,Chibuluma and Chambeshi mines in the Copperbelt.The cobalt concentrate are treated at Nkana mine.
Uses of Cobalt
Because of its magnetic properties and ability to withstand high temperature, it is used for:
- Manufacturing cutting tools eg. Knives ii. Manufacturing of magnets iii. Making diesels jets and steam turbines engines.
- Lead
It is a soft and dense metal that can be rolled or hammered into thin sheets.
Uses of Lead
- It is used as protective shield against radiation ii. For making bullets for guns iii. For making electric storage batteries iv. For making roofing materials v. For making pipes
- Zinc
It is a soft metal malleable and resists rust
Uses of Zinc
- Making roofing materials ii. For making toothpaste tubes iii. For making battery tubes
iv. For making paint tins
Lead and Zinc Mines
These mines were initially in Kabwe; however in 1994 they were closed due to the following reasons.
i. Decrease in production ii. Decrease in world market prices
- Coal
It is mined in Maamba Southern Province
Uses of Coal
- It is used in thermal power stations ii. It is used by processing plants such as Chilanga Cement, Nakambala Sugar Refinery
- Manganese
It is mined near Mansa in Luapula Province
Uses of Manganese
- It is used in dry cells factory
- It is used in alloy reserves in Central, Copperbelt Province and also near Chilanga
- Limestone
It is mined at Shimabala near Lusaka and Itawa in Ndola
Uses of Limestone
- Making paints ii. Treating water plants iii. Putting it on the field to neutralize the acidic soils
- Amethyst
It is mined in Southern Province open pits method and sorted by hands
- Gypsum
It is mined in Lochnivar in Kafue flat and Western Province near Ngoye falls in open pits.
Uses of Gypsum
- Making cements ii. Making proof tiles iii. Making fertilizer iv. Making paint
v. Making plasters of Paris wall paper
- Mica
It is mined in Lundazi, Choma and Mazabuka
Uses of Mica
It is used as insulator in stove oven glass windows
- Other minerals
- Iron ii. Diamond iii. Gold iv. Emeralds
H. Name the problems/challenges facing the mining industry in Zambia
i. Long distance to sea ports ii. Inadequate infrastructure eg. Houses for miners iii. Fluctuation market prices of minerals on the world market
- Shortage of mining spare parts
- High cost of production
- Poor road network
- Lack of capital to buy modernized equipments
- Name the solutions to the problems/challenges facing the mining industry in Zambia
- By forming mining support institutions eg. Metal Marketing Corporation(MEMACO)
- By encouraging private investment into mining industries
- Value addition to minerals by way of setting up mineral processing industries to make finished goods like electrical cables
- By improving road network
- By building enough infrastructure
- By forming companies that make mining spare parts
- Describe the role of government in the mining industry
- To encourage private investment into the mining industry
- Making of mining policies
- Making affordable mining taxes
- Improve road network
- Advertise potential mining prospects
- Support mining institutions
- Support value addition to minerals
H. Name the impact of mining on the environment
- Land degradation
- Displacement of humans and animals iii. Pollution of air, water, land and noise
iv. Destroys the natural vegetation
Mine waste disposal poses a health risk to humans and animals
![]()
