What is photosynthesis?
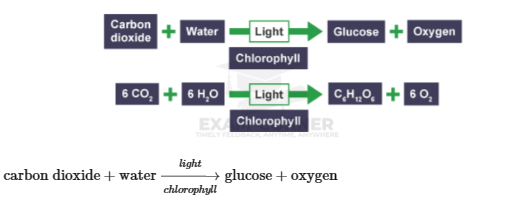
is chemical process that enables green plants to manufacture their own food molecules from the carbon dioxide and water molecules absorbed in the presence of a green pigment- chlorophyll that that absorbs light energy needed to break the water molecules down.
Plants make their own food using photosynthesis The food produced is the sugar called glucose. Food produced by plants is important, not only for the plants themselves, but for other organisms that feed on the plants.
Algae can also make their own food by the process of photosynthesis. Plant biomass will increase as a result of photosynthesis.
During photosynthesis, plants produce glucose and oxygen from the carbon dioxide and water.
and water, using light energy from the Sun.
Key fact
Be careful not to confuse this photosynthesis equation with respiration which is the reverse of this.
Photosynthesis is an endothermic reaction as it requires light energy to react carbon dioxide and water to produce glucose and oxygen.
The light energy required is absorbed by a green pigment called chlorophyll in the leaves. Chlorophyll is located in chloroplast in plant cells in the leaf.
Plant leaves are the main organs for photosynthesis.
The carbon dioxide required for photosynthesis comes from the air. It enters leaves through the stomata Water enters the plant through the roots, and is transported to the leaves in the xylem.
Oxygen is formed as a product. Some is used for respiration. During the day, provided the rate of photosynthesis is high enough, plant and algae give out oxygen.
Some of the glucose produced by photosynthesis is used for respiration.
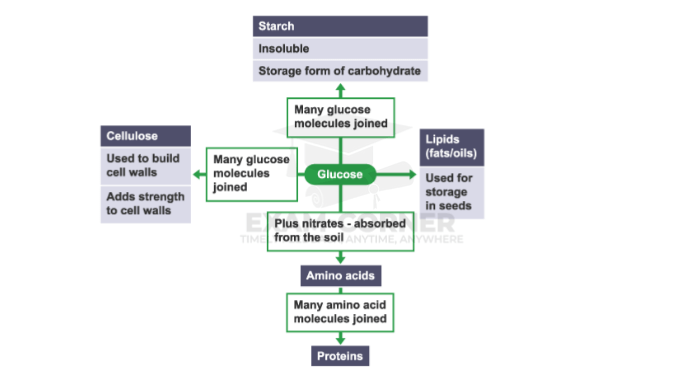
Glucose is the starting point for making the materials that plants need to live. These materials are used to make cell walls and other cell components and will enable the plant to growth and increase in biomass.
The glucose not used for respiration is used in the following ways:
Factors affecting photosynthesis – light intensity
There are several ways of measuring the rate of photosynthesis in the lab. These include:
- the rate of oxygen production (number of bubbles or volume of oxygen gas given off in a set time)
- the rate of carbon dioxide uptake
- the rate of glucose production
Several factors can affect the rate of photosynthesis:
- light intensity
- carbon dioxide concentration
- temperature
Light intensity
Without enough light, a plant cannot photosynthesise very quickly – even if there is plenty of water and carbon dioxide.
Increasing the light intensity increases the rate of photosynthesis, until some other factor – a limiting factor – becomes in short supply.
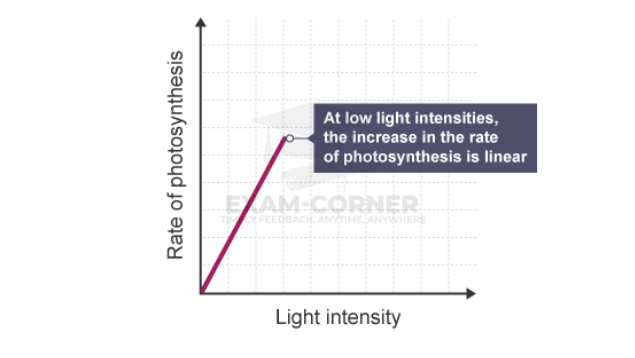
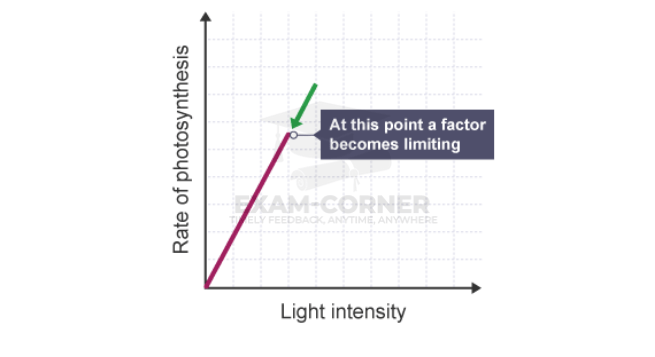
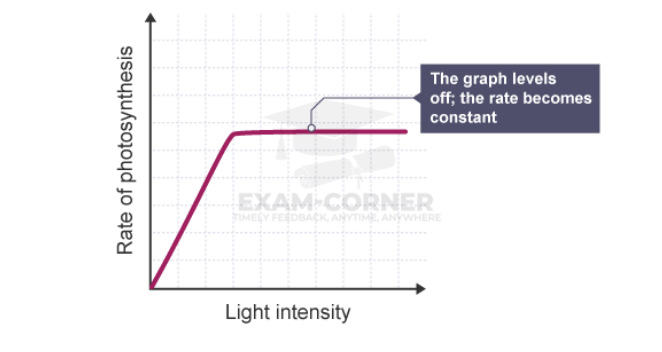
The rate of photosynthesis is directly proportional to the light intensity until another factor becomes limiting.
At very high light intensities, photosynthesis is slowed, but these light intensities do not occur in nature.
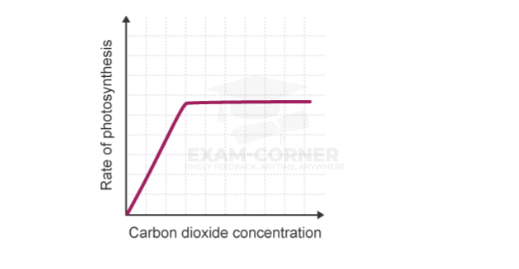
Carbon dioxide concentration
Carbon dioxide is one of the reactants in photosynthesis. If the concentration of carbon dioxide is increased, the rate of photosynthesis will therefore increase. At some point, another factor may become limiting, and this is shown by the plateau (flattened section) of the graph.
Temperature
The chemical reactions involved in photosynthesis are controlled by enzymes.
. As with any other enzyme-controlled reaction, the rate of photosynthesis is affected by temperature.
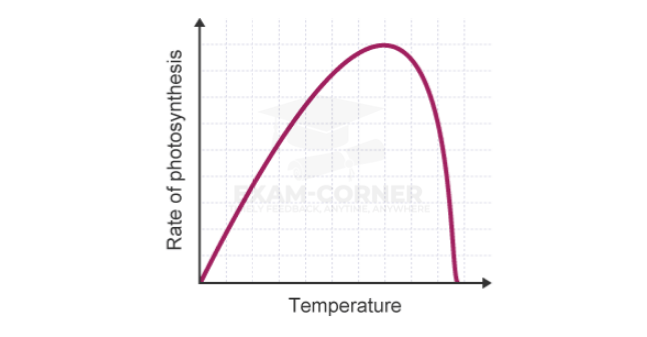
At low temperatures, the rate of photosynthesis is limited by the number of collisions between enzymes and substrate. As temperature increases the number of collisions increases, therefore the rate of photosynthesis increases. However, at high temperatures, enzymes are denatured.
and this will decrease the rate of photosynthesis.
Different factors limiting the rate of photosynthesis – Higher
If we look in more detail at the law of limiting factors, for instance, for the relationship between light intensity and the rate of photosynthesis:
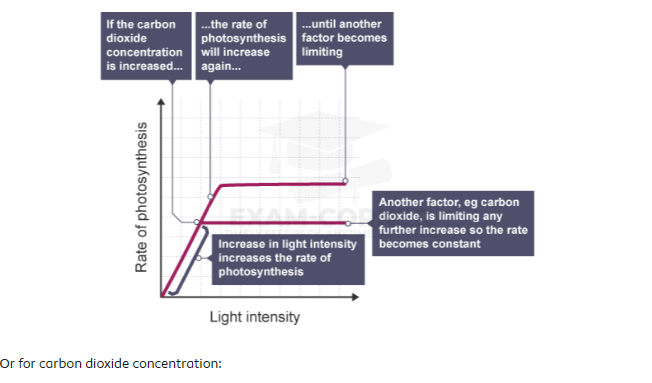
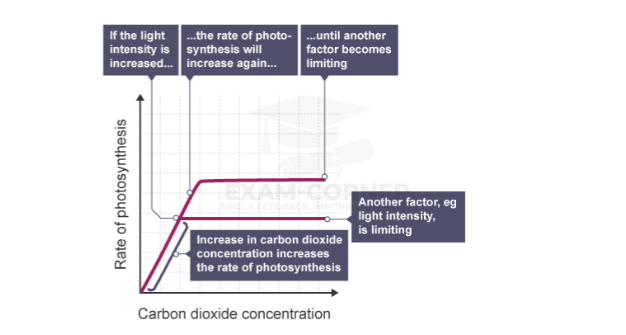
With the law of limiting factors, each factor does not work in isolation. Several factors may interact, and it may be any one of them that is limiting photosynthesis.
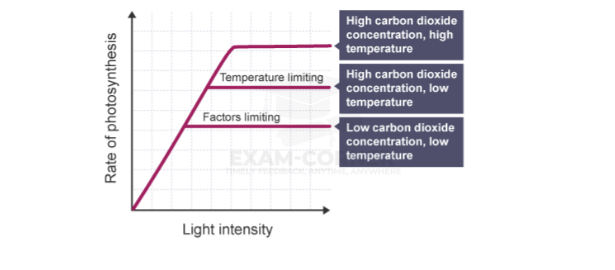
One example of how factors might interact:
The graph shows how carbon dioxide concentration and temperature interact with the effect of light intensity on photosynthesis:
- the rate of photosynthesis increases until factors becoming limiting
- if carbon dioxide concentration is increased, the rate increases further, and then another factor becomes limiting
- the rate can be increased further if the temperature is increased
- the rate increases again until another factor becomes limiting
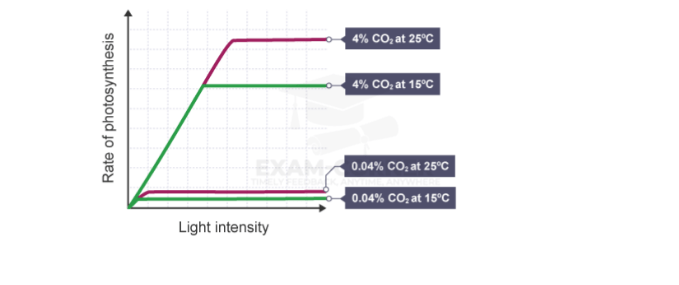
This graph shows the effect of temperature as a limiting factor at two different carbon dioxide concentrations of carbon dioxide:
![]()
